About this course
This practical and hands-on course is aimed at giving the engineering team a clear understanding of the maintenance plan development process to enable them to contribute to the process according to their specific roles and responsibilities.
Asset management is a strategic function of an organisation which ensures the highest level of physical asset performance. At the heart of this function are the maintenance plans that must manage the inherent failure modes of all of the organisation’s physical assets.
The maintenance plan development process is based on the optimum maintenance approach (OMA) methodology developed by Pragma with the specific objective of assisting companies in developing and improving the maintenance plans for their physical assets. The process consists of realising triggers, defining scope, analysing criticality and, based on this, deciding on the best approach to develop the maintenance plans.
These maintenance plans will turn the maintenance function into your organisation’s competitive advantage in gaining world class competitiveness.
Course Outcomes
Describe the maintenance plan development process and its various triggers
Conduct a criticality analysis to a basic asset
Perform a Failure Modes and Effect Analysis (FMEA) to a basic asset
Describe the difference between condition-based, usage-based, run-to-failure and design improvement tactics
Apply appropriate tactics to develop primary tasks, acceptable limits and secondary tasks
Package tasks for execution according to general Enterprise Asset Management System (EAMS) configurations
Improve tactics through continuous evaluation against relevant KPI’s
Introduction to Maintenance Plan Development
Gain a clear understanding of what maintenance plan development is by looking at different maintenance approaches, the benefits and the role players.
Understand the link between Pragma’s OMA methodology and reliability-centred maintenance (RCM).
Asset Criticality Analysis
Interpret a risk matrix and conduct a criticality analysis on a basic asset. Interpret the information from a criticality analysis to decide on the optimum maintenance approach (OMA)
Selecting the Optimum Maintenance Approach
Explore the three different maintenance approaches:
Basic Asset Care, Quick Tactics Development and Failure Modes and Effects Analysis.
Types of Tactics
Describe the difference between condition-based, usage-based, run-to-failure and design improvement tactics.
Task Development
Apply appropriate tactics to develop primary tasks, acceptable limits and secondary tasks.
Package Tasks
Package tasks for execution according to general Enterprise Asset Management System (EAMS) configurations.
Evaluate Tactics
Critically evaluate existing maintenance plans using evaluation guidelines. Set up effective maintenance plan key performance indicators (KPI’s).
Who should attend?
- Asset managers
- Maintenance managers
- Reliability engineers
- Production and operations managers
- Maintenance foremen and supervisors
- Maintenance engineers
- Maintenance technicians
- Maintenance planners
Format and duration
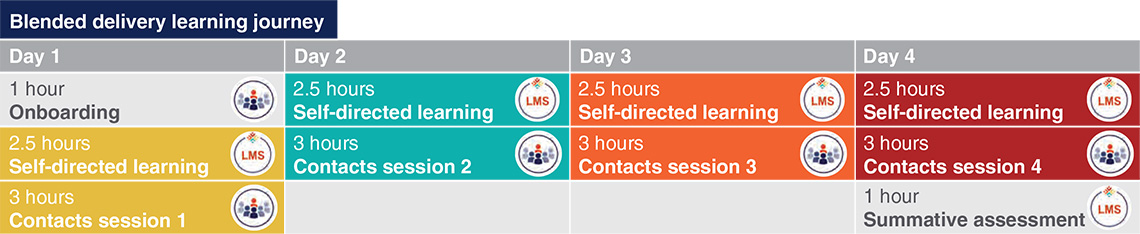
- 24 notional hours delivered either as blended learning or face-to-face
- Blended learning consists of
- 1 hr onboarding
- 4×3 hrs self-directed learning and assessment
- 1 hr summative assessment
- 3 day face-to-face classroom training. (Note that learners are required to bring their laptops to this training.)
Take-home tools
- Facilitated by an experienced asset management consultant
- Note that learners will complete a maintenance plan on an Excel document and therefore laptops are required during this training (or, at least one laptop per group).
Certification
- Learners completing this training can obtain SAAMA CPD points.