About this course
Give your maintenance management team a common understanding of what good maintenance looks like. This course will give them a logical model showing interfaces among all the elements, the best practices of each element and the benefits of doing it well.
Most maintenance engineers and supervisors end up managing maintenance activities without any formal training. This course is based on a logical model of maintenance management, covering the principles, best practices and benefits of each element, as well as the interfaces between them. The course is very interactive with lots of examples, exercises and guidelines, ending with a self-assessment and implementation roadmap.
Pragma has combined its 30 years of maintenance management experience with the accepted best practices from global standards, text books and guidelines to develop this course. If required, it can be customised to align with an organisation’s own maintenance blueprint and examples.
Outcomes
Describe good maintenance practices according to the Maintenance Management Model
Explain the maintenance objectives of improved performance and lower risk at optimal cost
Create a maintenance scorecard consisting of a balanced set of KPIs and targets
Describe the negative effects of reactive breakdown maintenance
Explain how the failure profile of components determine which maintenance tactics are applicable
Describe how maintenance work can be managed more effectively and efficiently
Explain how Maintenance can support Supply Chain to improve its material management
Make better contracting decisions and manage contractors more effectively
Explain the role of Production/Operations in ensuring reliable assets
Create a logical maintenance organisation with clear roles for everyone
Use the functionality of a maintenance information system to make better decisions
Interpret maintenance KPIs in order to identify opportunities for improvement
Develop a clear vision of what good maintenance looks like
Assess the Maintenance function and develop a maintenance improvement strategy
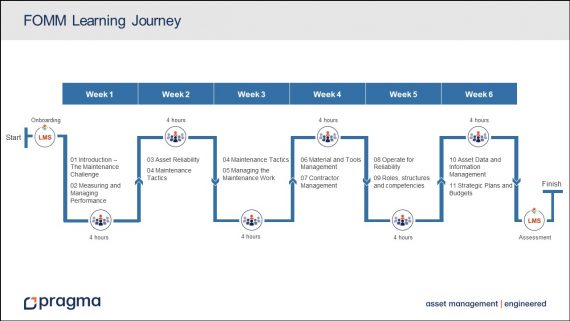
Introduction – The Maintenance Challenge
This module gives context to the course in terms of the global problem of ageing assets, terms and definitions, and the objectives of maintenance, using the Maintenance Management model as the driver.
Measuring and Managing Performance
This module introduces the PDCA cycle and the need for performance measurement. Key concepts are defined and a framework provided for a balanced maintenance scorecard. Finally, the role of daily meetings to review performance and drive improvements is discussed.
Asset Reliability
This module defines asset reliability and the role of
the reliability engineer. The different failure profiles
(age- related vs random), the P-F curve and the impact
of forced deterioration are unpacked. The calculation
and interpretation of MTBF is reviewed using
appropriate examples.
Maintenance Tactics
This module explains how asset criticality is defined and where it is applied. The four basic maintenance tactics are explained, how they are selected based on the components’ failure profiles, their packaging and implementation in the information system.
Maintenance Work Management
This module covers the 9-step process to manage maintenance work – the approval, planning, scheduling, allocation and execution of work. The roles of the people involved, the underlying best practices and the KPIs to measure the success of the process are explained using appropriate examples.
Material and Tools Management
This module gives learners insight into the Supply Chain processes and the effect on Maintenance and how certain bad maintenance practices (like squirrel stores) impact the effectiveness of material management.
Contractor Management
This module introduces some basic principles about making an outsourcing decision, selecting contractors and managing them as “external employees” according to the type of contract.
Operate for Reliability
This module covers the role of operational staff in asset reliability and performance improvement, by doing basic maintenance tasks like cleaning, inspections, minor repairs and assisting artisans with major work.
Roles, Structures and Competencies
This module gives an overview of a Maintenance structure and responsibilities. It covers all the important concepts related to training including competencies and assessment.
Asset Data and Information Management
This module explains the functionality of a typical maintenance information system. It covers the data management process for effective information, and how to manage changes to ensure up-to-date documentation.
Strategic Plans and Budgets
This module covers the strategic planning process – the development of an end-state maintenance vision, a 3-pronged gap assessment, and the development of a prioritised improvement strategy, with supporting budget.
Who should attend?
- Factory managers
- Engineering managers
- Managers maintenance
- Maintenance supervisors/ foremen
Format and duration
- 26 notional hours delivered via two options: 6x half-days of blended learning via a virtual classroom or 3 full days training in a physical classroom
- Online assessment
Take-aways
- A logical Maintenance Management Model
- Key considerations for implementing each element
- Maintenance management self-assessment
- Template for a maintenance management road map
Certification
- ECSA endorsed for 3 CPD points
- Aligned with the SAAMA designation for an Asset Management Practitioner